Insulin Resistance Evaluation using TyG Index and sNfL Responsiveness in Metabolic and Neurodegenerative Disorders.
The Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) index has emerged as a valuable tool in assessing insulin resistance, a critical factor in various health conditions. This index provides a reliable way to gauge the level of insulin resistance, which is linked to metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, as well as neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. By measuring the relationship between triglyceride and glucose levels in the body, the TyG index offers insights into an individual’s metabolic health and can help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment and prevention strategies.
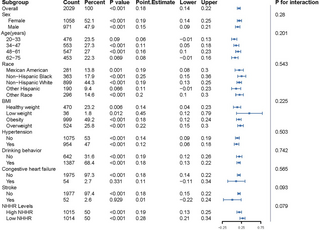
In a recent study, researchers have found that the TyG index is closely associated with serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels. sNfL is a sensitive biomarker that reflects neurodegenerative processes in the brain, making it a valuable indicator for conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. The correlation between the TyG index and sNfL levels suggests a potential link between insulin resistance and neurodegenerative disorders, shedding light on the intricate connections between metabolic health and brain function. This finding opens up new avenues for research and treatment approaches that target both metabolic and neurodegenerative conditions simultaneously.
Understanding the relationship between the TyG index and sNfL levels could pave the way for personalized medicine strategies that address both metabolic and neurological health concerns. By utilizing these biomarkers in clinical practice, healthcare providers can tailor interventions to target underlying insulin resistance while also monitoring neurological changes. This integrated approach holds promise for improving outcomes in patients with metabolic and neurodegenerative disorders, offering a more comprehensive and holistic approach to healthcare. As research in this area continues to evolve, the potential for innovative therapies and preventive measures grows, bringing hope for better management of these complex health conditions in the future.
AI-generated summary. Full credits:
Source: Plos.org.
Author: Tong Chen, Wei Zheng, Yan Zhang, Qian Xu.
Date: 2025-04-10T14:00:00Z.
Read more: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0321226.




Leave a Reply